[ad_1]
Is the sunshine an only youngster? Or was it born into a (incredibly, incredibly) significant family?
The response tells us additional than just how awkward getaway household reunions can be (if you think yours are poor, envision how considerably worse it would be with a several thousand sibling rivals). Following all, the sun’s origin tale is, finally, our personal. We’ve noticed big leaps in our understanding of how stars type, but, ironically, we even now have some fairly fundamental thoughts left about our nearest, dearest one. These kinds of as, whether the sun was born solo or alongside with a large passel of other stars.
Even with the sunlight getting near plenty of that we can virtually contact it, the largest dilemma with discovering its origin tale is that it’s previous. Born 4.6 billion decades ago, our star is properly into middle age and has wandered much from its ancestral home—some nameless, now-vanished “stellar nursery” of fuel that lengthy in the past dispersed or consolidated into stars.
We can not uncover that nursery, but we can nonetheless study about it. We have some proof of it, perhaps shockingly, in the variety of meteorites, some of which still carry clues about the gestational ecosystem around them throughout the birth of the solar technique. For illustration, isotopes of aspects like potassium inside of meteorites have explained to us wherever in the presolar nebula they shaped, and versions among meteorites can be applied to enable decide the nebula’s conditions well before the emergence of any planets.
With details from meteorites in hand and aided by state-of-the-artwork computer simulations, an worldwide crew of astronomers investigated the likely natal ecosystem of the sunlight and a short while ago released its success in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Modern society. Working with a clever line of reasoning, their research suggests the sun not only experienced numerous siblings but spawned in really a metropolitan community.
Stars are born in cosmic clouds referred to as nebulae, forming when their interiors collapse on to a central pilelike place that results in being the nascent star. Nebulae appear in a lot of styles and measurements, from small darkish globules to enormous big molecular clouds. How a star types in any specified nebula is significantly extra a story of character than of nurture.

For example, the nearby nebula Barnard 68 is a dim clot of cold fuel and dust—tiny grains of silicates (rocky content) and sophisticated carbon molecules similar to soot—relatively near to us in room, only a few hundred mild-decades absent. It is just one of my preferred objects an eerie, pitch-black ghostly mass that utterly blocks all gentle from stars behind it, like an opaque hole in the sky.
It’s only 50 percent a mild-12 months throughout (just about 3 trillion miles), with scarcely ample substance in it to make a single star a bit heftier than the sunlight. It’s possible in the middle of that approach now, and could transmogrify alone into a star in as minor as 200,000 yrs.
On the other conclude of the scale, we have the Orion B molecular cloud complex, a actually monumental web-site of lively star development that is over a thousand light-several years away and lots of hundreds of mild-several years throughout. It is beefy enough to make a staggering range of stars—at minimum 100,000 like the sunlight. The legendary Orion nebula, seen to the naked eye and the birthplace of hundreds of stars, is only one small element of this huge stellar factory.
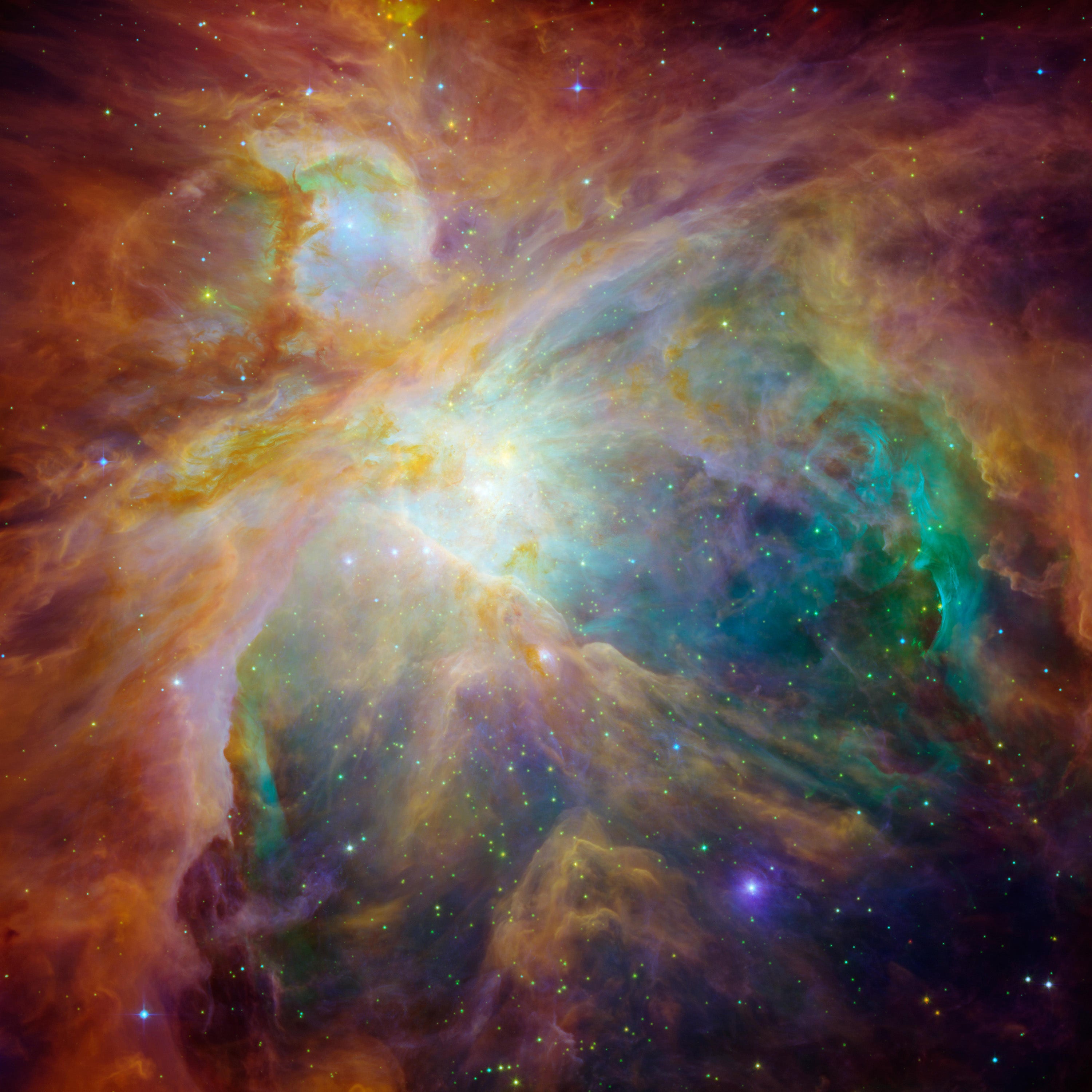
 

Giant clouds like this are somewhat uncommon but crank out stars on an industrial scale, while the lesser clouds are much less fecund but litter the galaxy. Just looking at those numbers statistically it’s not probable to discern the origin of the sun: it could have arrive from either type of stellar nursery.
Even so, these nebular environments are vastly various, which has an effect on the stars they build. Enormous stars found in a nebula have a big influence on their gestating siblings. They can blast out intense winds of subatomic particles—like the photo voltaic wind but ramped up way past 11. These winds can seed forming stars with major aspects like aluminum and magnesium. And later on, when they explode as supernovae, they fling a diverse combine of these elements, these types of as iron and cobalt, a very extended way.
Massive stars, though, are unusual. Probably one out of a hundred stars is significant ample to maintain this type of sway, and small nebulae basically really do not make them. That means, in principle, on the lookout at the chemical composition of the early solar procedure could explain to us in what kind of nursery the sunlight was born.
This was the aim of the freshly released investigate. The astronomers seemed at two aspects in particular: aluminum-26 and iron-60. Aluminum-26 is produced within substantial stars and blown out in their winds, while iron-60 is forged in the thermonuclear hell of an exploding star. Each things are radioactive, decaying into magnesium and cobalt, so carefully measuring the quantities of these daughter factors in pristine samples from the earliest days of the solar system—from meteorites, that is—can convey to us about the natural environment in which the sun shaped.
For their new analysis, the worldwide staff of scientists used the physics of nebulae and star formation to simulate a sunlike star’s beginning in a assortment of environments, from nebulae that contains really couple stars (a proxy for smaller clouds) up to enormous kinds with many thousands. Subsequent, they calculated the elemental composition of the proto-proxy-presolar disk that emerged in each a person, then as opposed these virtual yields towards what is truly calculated in meteorites.
Their final results reveal that as it shaped in its natal disk, the early sunlight was very likely pummeled by powerful winds and supernovae explosions—both sourced from large stars. That suggests the solar nursery was additional like the Orion complex than Barnard 68.
In other words, the sunlight was possibly more of a downtown city kid than a rural modest-city star. Of class, with its nebular nursery gone, we cannot verify this effortlessly. Just after all, you just can’t go dwelling all over again.
And what of the sun’s siblings, the 1000’s of other stars in its prolonged loved ones? Like the sun, they as soon as nestled alongside one another like a litter of puppies, but possible wandered out on their very own eons in the past, and are now orphaned, scattered across the galaxy. Even now, astronomers do look for them—ones with the exact age and composition as the sun—so that we can understand more about our parent star.
A reunion is quite unlikely. If we want to see a relatives album, we’ll just have to place it collectively ourselves.
This is an feeling and evaluation write-up, and the sights expressed by the creator or authors are not automatically those people of Scientific American.
[ad_2]
Resource link


