[ad_1]
Researchers have cultivated monkey embryos in the laboratory very long adequate to view the starting of organ development and the enhancement of the anxious procedure — milestones that are hard to observe in embryos expanding in the uterus. The embryos reached the age of 25 days, generating them what might be the oldest primate embryos to be developed exterior the womb.
Independent teams explained the conclusions in different papers in Mobile on 11 Could.
“It’s really amazing,” says Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz, a developmental biologist at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, who was not associated in the study. “It’s heading to carry a ton of new insights.”
Heading 3D
Handful of issues are as tough as preserving lab-grown embryos alive for for a longer time than a few of weeks — most volume to absolutely nothing extra than a blended bag of cells in a dish. Formerly, both teams experienced managed to culture monkey blastocysts — balls of dividing cells — in Petri dishes for up to 20 times. Earlier that point, all the embryos experienced collapsed, generating it difficult to see a lot more advanced levels of their enhancement, these kinds of as early indicators of the anxious method and organ development.
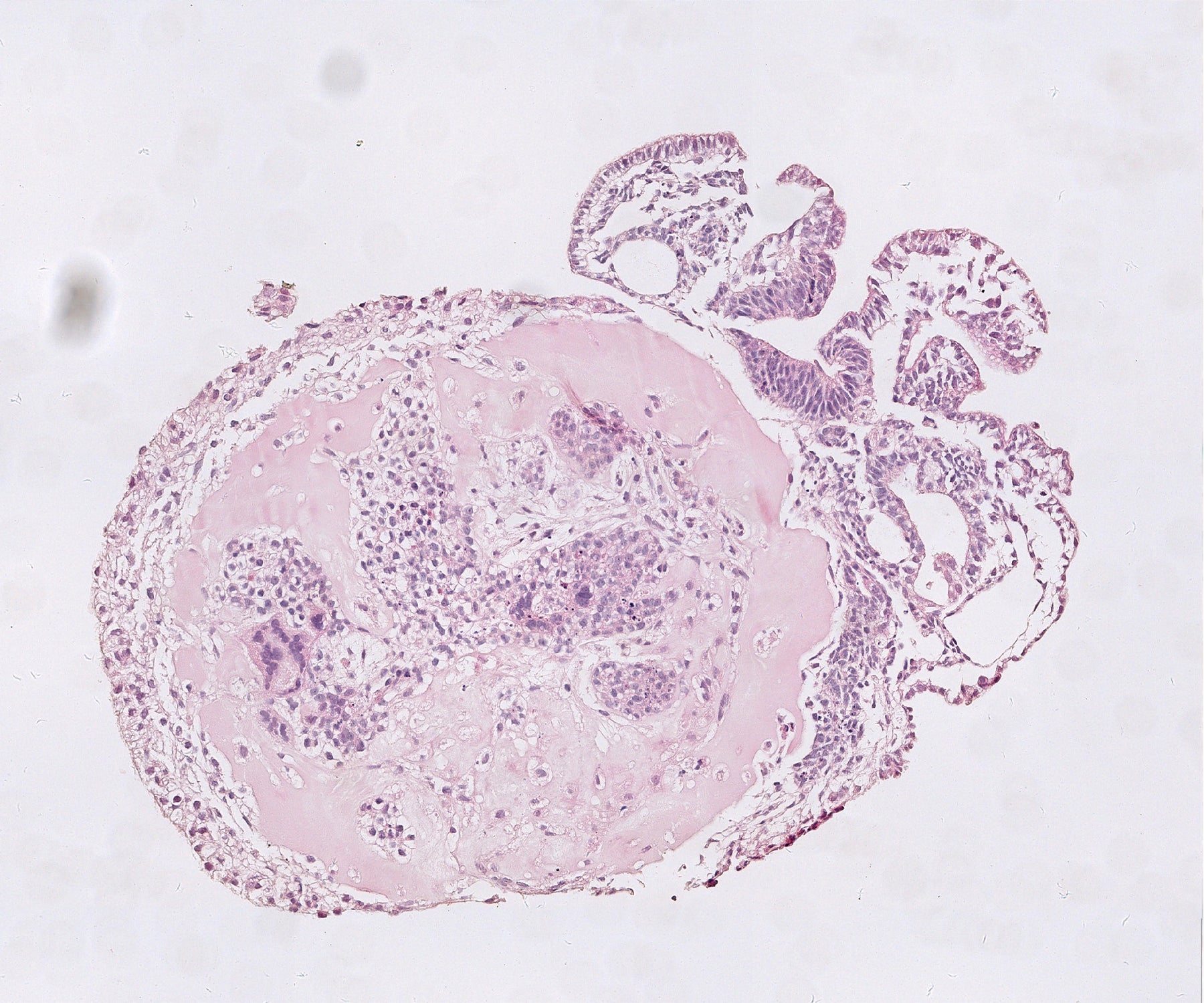 

But in the new experiments, the researchers grew monkey embryos in smaller vials of tradition medium, which authorized the embryos to mature in three proportions as they would within the womb. Equally groups coaxed their embryos to endure for 25 times just after fertilization. Neither the authors nor outside the house scientists contacted by Nature knew of more mature primate embryos developed in the lab.
Viewing organs just take shape
Hongmei Wang, a developmental biologist at the Point out Key Laboratory of Stem Mobile and Reproductive Biology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, and her workforce attained egg cells from feminine cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) and fertilized them in the lab with sperm collected from their male counterparts. A 7 days later on, they put the ensuing blastocysts into a gel-like substance in smaller cylindrical containers and watched them develop for 25 days.
Approximately two months just after fertilization, much more than 50 percent of the embryos experienced an embryonic disk — a flat mass of cells. These disks ultimately fashioned the a few main cell levels of the entire body: the endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. The lab-grown embryos also showed genetic options related to those noticed in all-natural monkey embryos within just the very same time frame.
By working day 20, the embryos experienced formulated a neural plate — 1 of the early hallmarks of the anxious method. As in pure embryos, this plate thickened and bent into a tube that kinds the basis of the brain and spine. Wang and her staff also pinpointed cells that would at some point become motor neurons. The insights gleaned from the lab-grown embryos will assistance scientists to establish a better being familiar with of early embryo enhancement in primates, says Wang.
Where blood is born
In the second research, Tao Tan, a developmental biologist at Kunming University of Science and Know-how in Yunnan, China, and his colleagues also created blastocysts from cynomolgus monkey eggs and sperm. But they utilised two unique types of cell lifestyle to present more robust mechanical guidance for the embryos, and added glucose to supply them with electricity as they grew.
As in Wang’s examine, most of the cells in the cultured monkey embryos have been the very same type as all those typically viewed in organic embryos 18 to 25 days soon after fertilization. When Tan and colleagues took a closer glimpse at the embryos’ mesoderm cells, they discovered that some had differentiated into coronary heart muscle mass cells and other individuals had matured into cells found in the lining of blood and lymphatic vessels. The workforce also pinpointed cells that build into connective tissue and types that form the foundation of the digestive program.
The researchers also found indications that blood cells and their elements have been beginning to acquire shape in the yolk sac, which materials embryos with nutrition. “We were being deeply amazed,” says Tan. These blood cells “are just about unachievable to receive throughout human embryonic improvement.”
Naomi Moris, a developmental biologist at the College of Cambridge, Uk, says that the scientific tests existing an crucial move in developing approaches that can sustain embryos outside the womb for lengthier than experienced been possible beforehand. But she cautions that there is even now a prolonged way to go just before lab-grown embryos will look and behave like the real thing. “They nonetheless seem a little bit unique to how we would assume [them] to look at these levels,” suggests Moris, who was not included in the investigate. “There’s certainly continue to scope for improvement.”
This posting is reproduced with permission and was to start with printed on May well 11, 2023.
[ad_2]
Supply website link


