[ad_1]
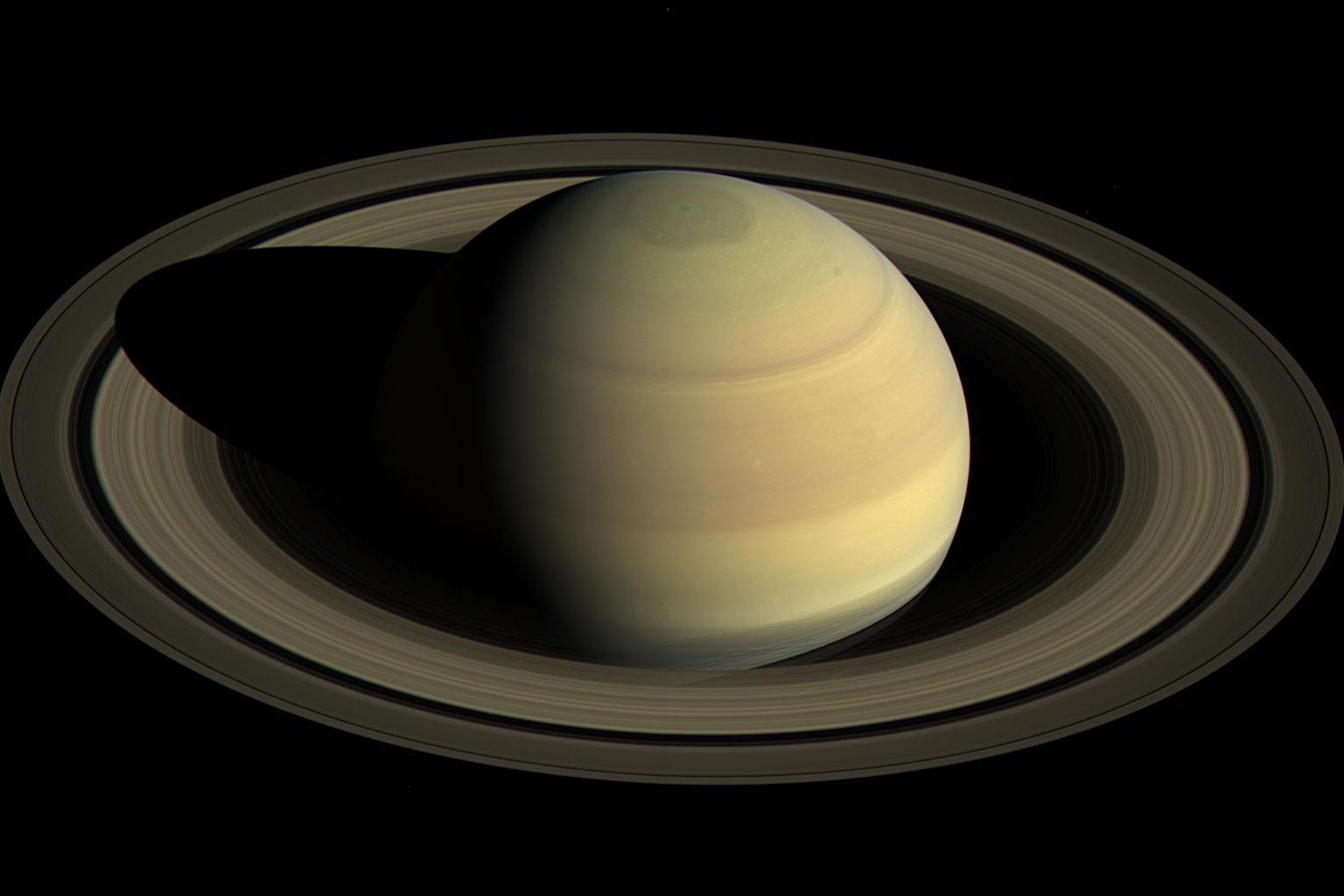
Saturn is the jewel of the solar technique, with its magnificent rings and retinue of strange moons. It is the faintest of the naked-eye planets—technically Uranus is often dazzling plenty of to see, though you have to have excellent eyesight and a pretty dim site—but nonetheless relatively uncomplicated to pick out between the stars.
If you are an early riser (or a late partier), then now is a first rate time to glimpse for Saturn, not mainly because it is brighter or nearer to Earth than normal but mainly because it’s produced some news recently. New investigation implies its rings are rather youthful, cosmically talking, and astronomers have also just announced the discovery of a whole passel of very small Saturnian satellites that make the world the latest history holder for the biggest selection of moons.
Saturn presently crests the horizon early in the early morning nearby time and about an hour afterwards rises substantial more than enough to place very low in the southeastern sky. If you get up soon prior to dawn, it’ll be about 25 levels higher than the horizon, or roughly 2.5 occasions the width of your outstretched fist—a universal unit of evaluate among the astronomers. Never confuse it with the nearby star Fomalhaut, which is nearer to the horizon than Saturn and has practically specifically the very same brightness. Jupiter is closer to the jap horizon (down and to the left of Saturn, for Northern Hemisphere observers), but it is 15 moments brighter and considerably less complicated to location.
If you’d like to stay clear of a predawn viewing, in this case, waiting is fine, much too: Saturn’s rings and moons are not likely to vanish (on human timescales in any case). And as summer season progresses, the earth rises earlier and gets larger in the sky at a additional sensible time. By late June it rises about midnight in several areas, for illustration, and by late August it reaches the sky viewing sweet place: it rises at sunset and stays up all night.
Through binoculars, Saturn can appear elongated or oval-shaped since of its rings. The sharper watch from a modest telescope will expose the rings far more obviously. Applying just one, you may well even spot a pair of the planet’s moons its premier, Titan, is even larger than Mercury and ordinarily appears as a faint “star” adjacent to Saturn.
If you do courageous the early several hours to get a search at the gas giant, acquire a moment to contemplate what you’re definitely observing. The pale, resplendent orb, so little in our sky, is a behemoth that is nine situations wider than Earth and 95 times much more massive. And even with centuries of observations, we’re still learning about this ringed marvel.
Saturn is legendary amongst its planetary siblings due to the fact of its rings, of course. Jupiter, Uranus and Neptune all have rings, much too, but all those are skinny, faint and tough to see devoid of spacecraft or potent telescopes. Saturn’s rings extend an extraordinary 175,000 miles (282,000 kilometers) across—three quarters of the length among Earth and our moon!
Even however they seem to be sound, Saturn’s rings are in fact composed of countless chunks of approximately pure h2o ice, most likely the remnants of a shattered moon. The premier chunks are probably less than 10 meters across—with most remaining more like the sizing of the ice cubes you set in your beverages. Even though the rings have not appeared to adjust much at all due to the fact individuals begun observing them by way of telescopes in the 1600s, their age and longevity have been contentious challenges amid authorities for a lot of that time.
A lot more not too long ago, evidence has been mounting that the rings are far younger than the planet’s individual around 4.5-billion-yr age. The Cassini mission supplied a great deal of the information for this the spacecraft orbited the earth for 13 a long time and sent a wealth of information and facts to Earth.
New exploration, just revealed in the planetary science journal Icarus, reinforces the idea that not only are the rings youthful, but also they won’t very last forever.
Micrometeoroids—tiny space rocks zipping close to the solar system—were key to this new chronology. When they strike particles in Saturn’s rings, there are two in general penalties. One is that micrometeoroid dust pollutes and darkens the rings’ pristine water ice. The other is that people little collisions sap orbital energy from the ring particles, which answer by relocating inward toward Saturn. With each other, these outcomes must make the ring particles increase grimy over time and eventually rain down onto Saturn alone.
With Cassini info in hand, the researchers set quantities to these effects, finding that the rings are possible no older than about 120 million a long time, which is very young for a planetary process. To set that into perspective, if early Cretaceous dinosaurs had invented telescopes, they would’ve found Saturn devoid of rings!
The scientists also uncovered the rings are eroding at a rate that signifies they’ll vanish someday amongst 15 million and 400 million several years from now. That is a long time in human terms but nevertheless only a fraction of the photo voltaic system’s age.
Ironically, though Saturn’s rings are fading absent, it seems to have a developing selection of moons. That is not the scenario literally or physically—we’re just obtaining improved at finding them.
Scientists have just introduced a new passel of 62 moons about Saturn, bringing the planet’s full to additional than 140, blowing appropriate earlier Jupiter’s former document-keeping rely of about 90.
The researchers basically spotted quite a few of these moons in observations taken in 2019 employing a clever procedure to greatly enhance their visibility, but these very small satellites ended up extremely faint and did not move incredibly considerably in concerning observations. To affirm them, the astronomers needed to get a lot more knowledge. In excess of the past two decades they’ve done just that and nailed down the fact of the moons, most of which are only a couple of kilometers throughout.
How a lot of moons could possibly Saturn really have? Well, that is dependent on what you mean by “moon.” There are hundreds, certainly—maybe hundreds bigger than a kilometer or so. But if you count every single ring particle as a moon, then the remedy is trillions. The issues in this article is we really don’t have a superior definition of what makes a moon, particularly with regard to what the decreased sizing limit may be. So in that perception, attempting to make your mind up which world has the most is a bit foolish.
But continue to, if you venture out early and gaze at Saturn in the predawn spring skies, don’t forget you are now armed with awareness that would make the astronomers of just a couple a long time back jealous. Hundreds of moons as major as mountains circle Saturn. Its rings are young and fleeting. In a really true perception, we’re lucky to be about to see them at all.
[ad_2]
Source url


