[ad_1]
Artificial intelligence can structure an autonomous robot in 30 seconds flat on a laptop computer or smartphone.
It is not very time to stress about just anyone staying ready to create the Terminator even though waiting around at the bus prevent: as described in a the latest analyze, the robots are uncomplicated devices that scoot together in straight lines devoid of executing far more elaborate responsibilities. (Intriguingly, even so, they normally appear to be to establish legs fairly than an arrangement that consists of wiggling, transferring like an inch worm or slithering.) But with a lot more do the job, the technique could democratize robot style, says research writer Sam Kriegman, a personal computer scientist and engineer at Northwestern College.
“When only substantial organizations, governments and large tutorial institutions have adequate computational electricity [to design with artificial intelligence], it definitely limits the variety of the inquiries currently being requested,” Kriegman says. “Increasing the accessibility of these resources is some thing which is seriously enjoyable.”
AI can now generate essays and push cars and trucks, so design and style might seem to be like a sensible next step. But it is not easy to make an algorithm that can successfully engineer a serious-planet solution, states Hod Lipson, a roboticist at Columbia College, who was not concerned in the investigation. “Many questions remain,” Lipson states of the new research, “but I assume it’s a big step forward.”
The method makes use of a model of simulated evolution to create robots that can do a specific task—in this case, ahead locomotion. Beforehand, producing advanced robots concerned producing random variations, screening them, refining the best performers with new versions and testing those versions yet again. That needs a whole lot of computing ability, Kriegman suggests.
He and his colleagues rather turned to a process referred to as gradient descent, which is extra like directed evolution. The approach starts off with a randomly created body design for the robotic, but it differs from random evolution by offering the algorithm the means to gauge how perfectly a specified overall body plan will perform, in contrast with the ideal. For every iteration, the AI can household in on the pathways most possible to lead to success. “We presented the [algorithm] a way to see if a mutation would be superior or poor,” Kriegman claims.
In their computer system simulations, the scientists began their robots as random styles, gave the AI the goal of developing terrestrial locomotion and then set the nascent bots unfastened in a digital environment to evolve. It took just 10 simulations and a issue of seconds to get to an optimum state. From the first, nonmoving physique approach, the robots have been capable to begin relocating at up to .5 system size for every next, about fifty percent of the ordinary human going for walks speed, the scientists described on Oct 3 in the Proceedings of the Countrywide Academy of Sciences United states of america. The robots also regularly advanced legs and began walking, the workforce found. It was spectacular that with just a number of iterations, the AI could create a thing useful from a random sort, Lipson claims.
To see if the simulations labored in observe, the scientists developed illustrations of their greatest-undertaking robot by 3-D printing a mold of the layout and filling it with silicone. They pumped air into little voids in the shape to simulate muscle mass contracting and growing. The ensuing robots, every single about the dimensions of a bar of soap, crept alongside like blocky very little cartoon people.
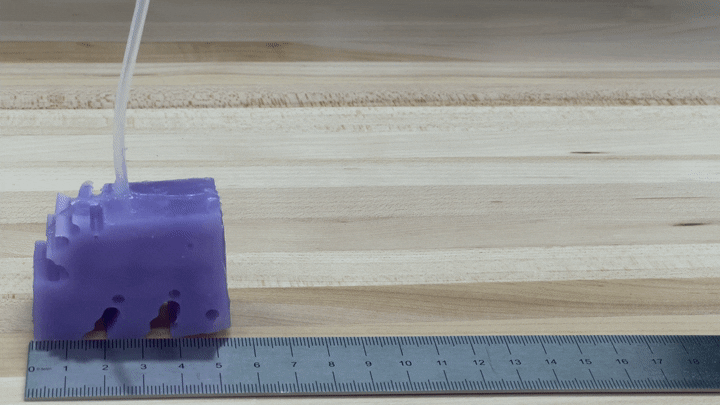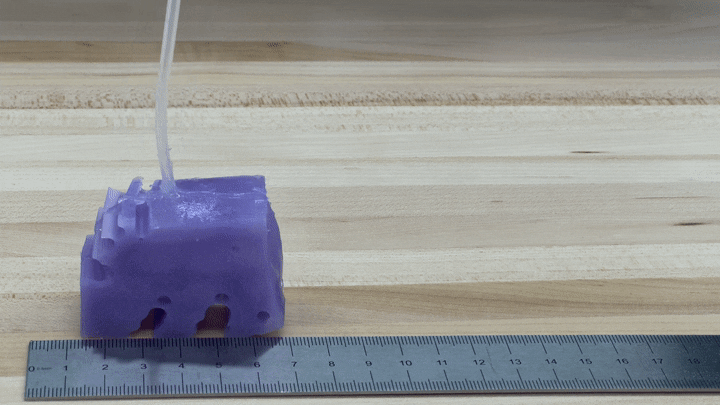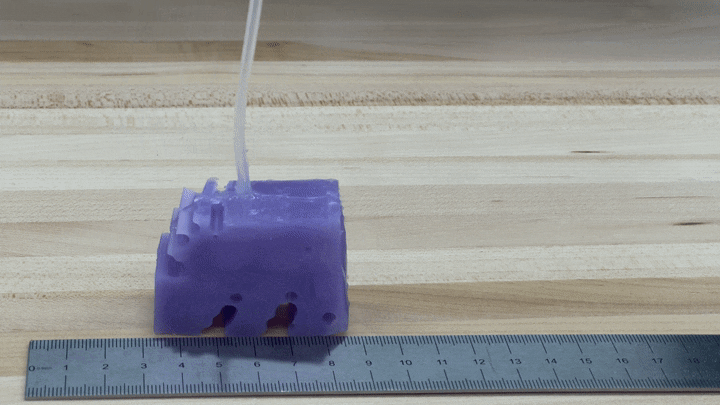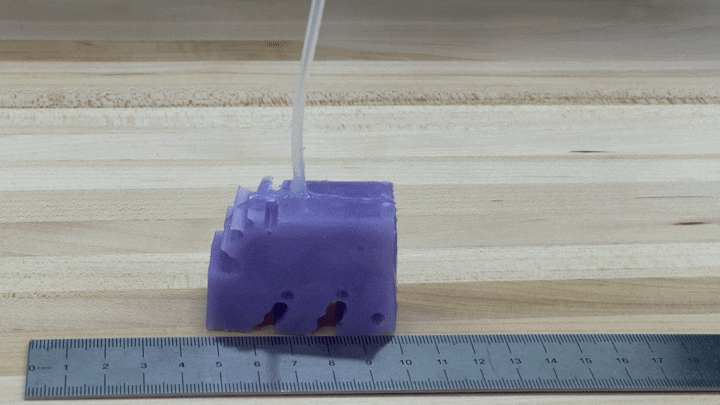 

“We’re truly energized about it just relocating in the ideal path and transferring at all,” Kriegman states, mainly because AI-simulated robots do not necessarily translate into the true planet.
The research represents a action towards a lot more highly developed robotic design and style, even though the robots are really simple and can finish only a single activity, claims N. Katherine Hayles, a professor emerita at Duke University and a investigate professor at the College of California, Los Angeles. She is also creator of How We Turned Posthuman: Virtual Bodies in Cybernetics, Literature, and Informatics (University of Chicago Press, 1999). The gradient descent technique is previously very well-proven in coming up with artificial neural networks, or neural nets—approaches to AI impressed by the human brain—so it would be impressive to place brains and bodies together, she claims.
“The actual breakthrough here, in my feeling, is likely to be when you acquire the gradient descent procedures to evolve neural nets and hook up them up with an evolvable body,” Hayles claims. The two can then coevolve, as transpires in dwelling organisms.
AI that can design and style new items could get people unstuck from a assortment of pernicious complications, Lipson suggests, from developing the next-technology batteries that could help ameliorate local climate transform to finding new antibiotics and prescription drugs for presently uncurable ailments. These simple, chunky robots are a step towards this objective, he claims.
“If we can style and design algorithms that can layout items for us, all bets are off,” Lipson claims. “We are likely to encounter an outstanding enhance.”
[ad_2]
Supply link


