[ad_1]
December 6, 2023
5 min browse
A modern analyze finds various combos of microbes in the vaginal microbiome might impact health and fitness outcomes this kind of as possibility of sexually transmitted condition and preterm start
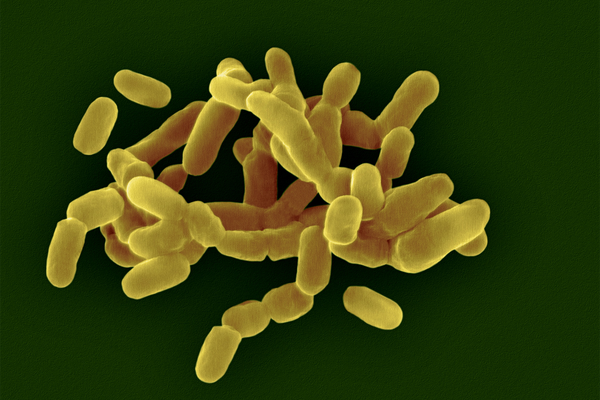
Even though involved with the problem bacterial vaginosis, Gardnerella vaginalis is a microorganisms species that may possibly be isolated from ladies devoid of any signs or signs and symptoms of an infection.
Of the a lot of microbial communities in the human overall body, the vagina’s microbiome is exclusive. Even though amplified range is crucial to microbiomes such as these in the intestine or mouth, the vagina has been imagined to thrive when it has less bacterial species overall and more of one certain species crucial to vaginal health, Lactobacillus crispatus.
But a new examination released previous 7 days in Microbiome exhibits a more intricate photo. Of the 28 bacterial species popular to the vagina, experts identified 135 exceptional combinations of strains of individuals species, each of which has diverse capabilities and cohabits with other strains. “So the range exists we just under no circumstances experienced a possibility to appreciate it,” suggests review co-author Jacques Ravel, a professor of microbiology and immunology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and performing director of the Institute of Genome Sciences at the college. The results demonstrate what the diverse pressure mixtures might do in the body—and how they could perform a function in a person’s susceptibility to sexually transmitted diseases and risk of preterm start and their in general well being.
The microorganisms that colonize the vagina defend in opposition to infection. An imbalance of these microbes are related with specific bacterial infections and healthcare situations, such as bacterial vaginosis (BV), a unpleasant affliction that influences about 30 p.c of females involving the ages of 14 and 49 in the U.S. Bacterial vaginosis is pretty sick-defined, Ravel states. While one particular individual’s an infection may existing very similar signs to another’s, together with itching and an odorous discharge, “Microbiologically it could be very distinct,” Ravel claims. Past research has identified two certain imbalances of the vaginal microbiota that normally guide to bacterial vaginosis. In the new examine, Ravel’s group sequenced just about 2,000 vaginal metagenomes—the genetic content of all the microorganisms in an natural environment. This unveiled nine communities of microbes that were particularly linked to bacterial vaginosis.
Some species of Lactobacillus, specifically L. crispatus, are recognized to be affiliated with a reduced risk of BV. Persons who have fewer vaginal L. crispatus could also have a better possibility of getting and spreading HIV. The exploration located quite a few strain combos of the species that can provide safety from BV. The function of a further common species in the very same genus, L. iners, is considerably less recognized. The new assessment indicated that some females with L. iners were being very vulnerable to BV when other people had been not—the team was ready to show that a single unique mixture of L. iners strains was much more often noticed in BV instances. This degree of comprehending could help medical doctors establish pitfalls of creating the condition primarily based on a certain vaginal microbiome composition, says guide research writer Johanna Holm, an assistant professor of microbiology and immunology at the College of Maryland Faculty of Medication and a college member of the Institute for Genome Sciences.
The review also reaffirmed that a larger range of Gardnerella species, other nicely-recognized BV-associated micro organism, had been joined with the issue. Owning loads of distinct species of Gardnerella and hence a significant selection of strains and pressure mixtures was much more linked to BV than owning much less species. Other experiments have looked into the partnership amongst Gardnerella strains and bacterial vaginosis but not with as a lot of samples as the current paper incorporated, Holm states.
Persons with bacterial vaginosis are usually taken care of with antibiotics—an intervention that has not improved considering the fact that the 1980s, suggests Craig Cohen, a professor in the office of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences at the College of California, San Francisco, who was not involved in the paper. It’s unclear why some men and women practical experience recurring bacterial vaginosis following antibiotic treatment, but Cohen suspects this may be connected to the presence of various strain mixtures contributing to the affliction. Holm says the flaws of antibiotic treatment for BV is in element because of to the field’s incapacity to precisely define bacterial vaginosis.
“BV will come in a large amount of flavors,” states Melissa Herbst-Kralovetz, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the College of Arizona College of Medicine–Phoenix, who was not associated in the paper. Although the new paper is a “great first step” in comprehension vaginal bacterial communities and their purpose, she suggests that extra target is wanted on other critical BV related organisms that may perhaps enjoy a role in the ailment.
Pretty much a few quarters of the study’s participants determined as Black, a inhabitants which has a larger threat of vaginal dysbiosis—the scientific phrase for an imbalance in vaginal microbiota. The results could be additional difficult if other racial and ethnic groups had been integrated at higher percentages, Cohen suggests. Demographic facts these types of as socioeconomic, residence and education facts could further increase the interpretation and examination, Herbst-Kralovetz claims.
The scientists are now expanding their current knowledge set to consist of vaginal microbiome samples from populations that are fewer examined. The workforce is also investigating how pressure combinations are afflicted by cleanliness techniques this sort of as douching and working with menstrual merchandise, as very well as by sexual behaviors these types of as working with condoms or acquiring many partners.
“What our examine implies,” Holm claims, is that the severity of BV “may differ relying on what ‘type’ of BV local community you have.” Future therapies might be personalized to handle these specific neighborhood varieties, she provides. Ravel and Holm hope that a superior understanding of the bacterial communities powering BV will enable with these sorts of specific cure as nicely as novel prognosis strategies.
Clinicians don’t routinely evaluate the vaginal microbiome to diagnose BV, Herbst-Kralovetz suggests. Usually they use Amsel criteria—the recent clinical diagnostic conventional also utilised in the study—to detect the affliction by the existence of loads of slender vaginal discharge, germs-covered vaginal cells termed clue cells, a fishy odor or vaginal fluid pH degrees above 4.5. Often molecular diagnostics that pinpoint BV-involved organisms are made use of, but these can be tough to interpret, Herbst-Kralovetz suggests.
Cohen suggests this kind of clinical purposes could involve a self-administered dipstick to examination for an ideal balance of vaginal microbes. Early exploration indicates that probiotics designed to encourage advancement of good microorganisms may also impact the protective skills of the vaginal microbiome—Ravel’s lab is at this time involved in developing probiotic therapeutics for urinary tract an infection and BV.
Despite the fact that the new examine was ready to discover distinctive strains of bacteria in the vagina much more specifically, Cohen claims that scientists now need to unpack no matter whether these pressure mixtures matter to well being. “It’s likely to just take a ton additional get the job done to realize the interactions of the microbial and the human metagenome and its outcome on overall health and effectively-remaining.”
[ad_2]
Source url


