[ad_1]
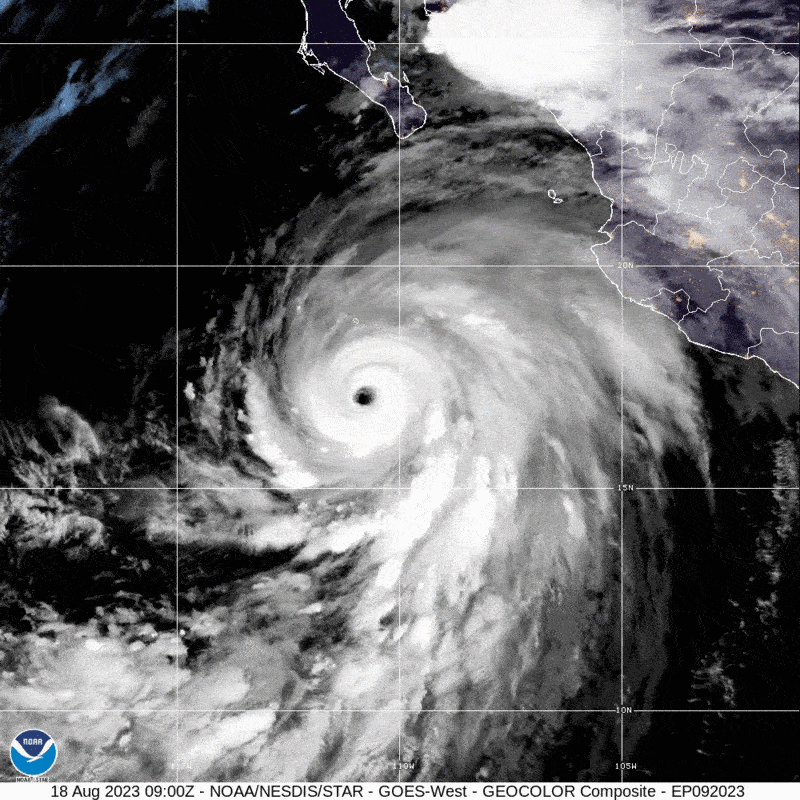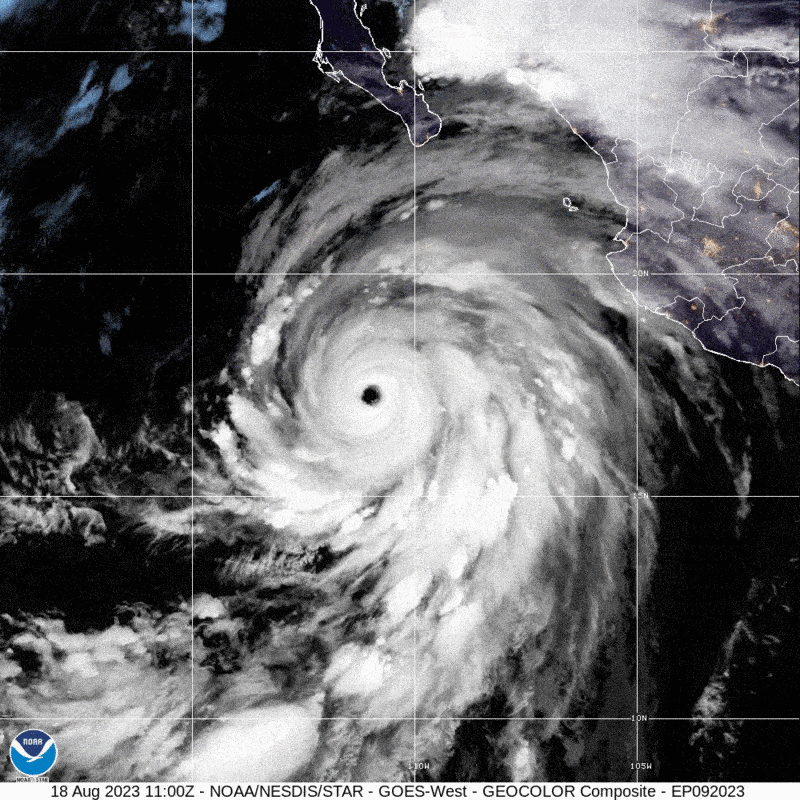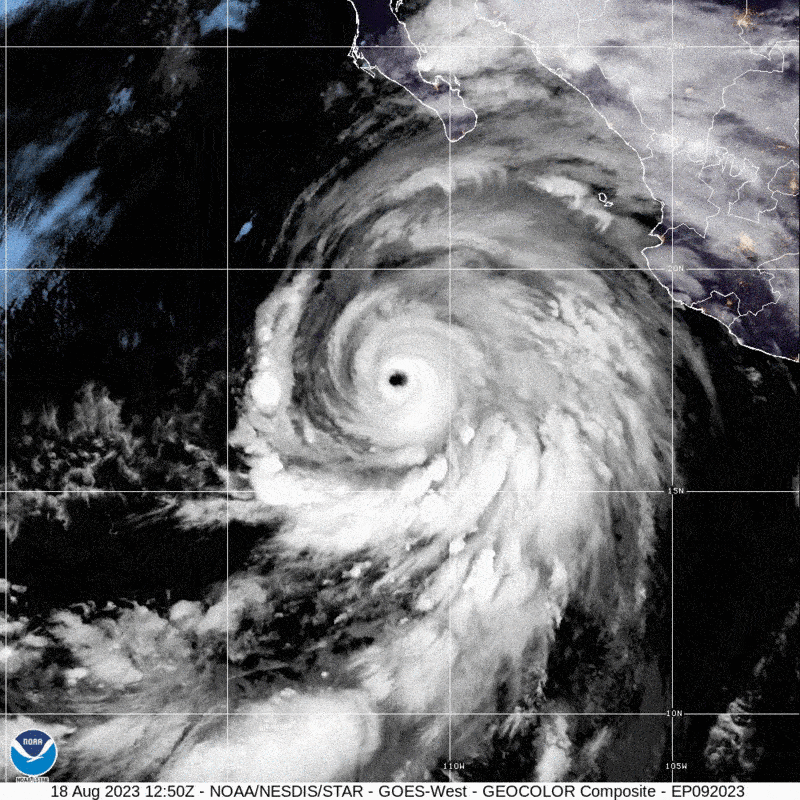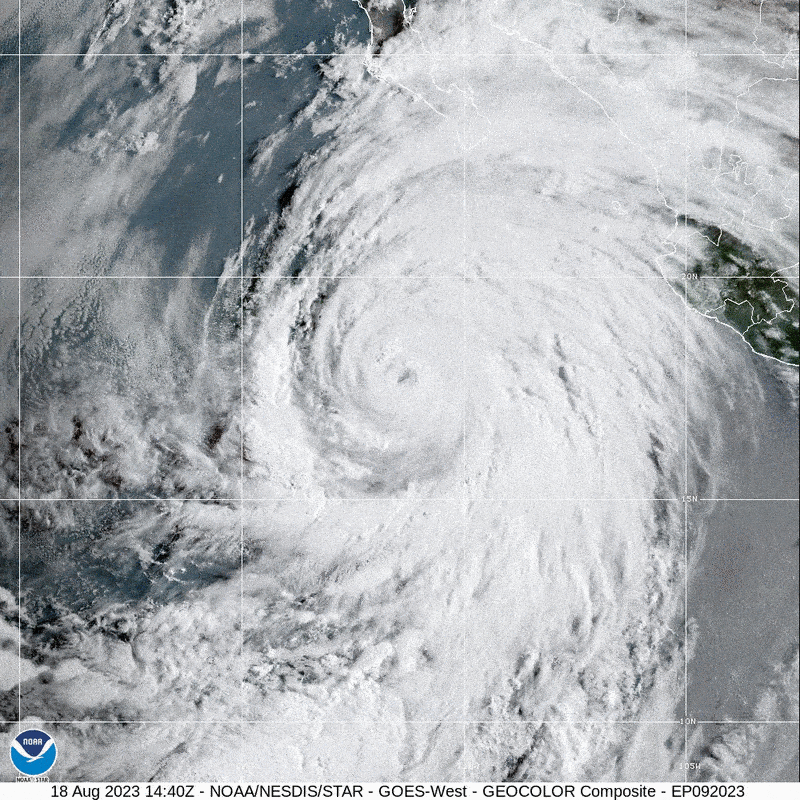
Southern California has not viewed a direct strike from a tropical storm due to the fact 1939, when an unnamed tempest produced landfall at Extensive Seaside on September 25 and caused dozens of fatalities. Now the state could see a different tropical storm make landfall as Hurricane Hilary barrels towards Baja California and the U.S. Southwest. The Nationwide Hurricane Centre (NHC) has issued the initially at any time Tropical Storm Check out for the West Coast.
Irrespective of where by Hilary hits, a extensive spot of southern California, southern Nevada and western Arizona are envisioned to expertise heavy rains that pose a important chance for flash flooding. Extra than a year’s truly worth of rain could drop on some parts in just a few of times.
Hilary fashioned off the western coast of Mexico in the jap Pacific Ocean on Wednesday. Concerning Thursday and Friday the storm fast intensified from a Category 2 hurricane to strong Group 4, fueled by ample heat ocean waters that fed into Hilary’s convection and a lack of the crisscrossing winds that can hamper a storm. Hilary is predicted to weaken as it approaches land for the reason that it will be moving over colder waters.
Meteorologists at present forecast that the storm will make landfall in Baja California as a hurricane. Incredibly smaller deviations in its keep track of could see it skirt the coast of Mexico and rather strike California, even so. By that place in the latter situation, Hilary may weaken to a tropical storm—or maybe a publish-tropical storm, a form that is fueled by distinctive atmospheric procedures but that can still pack just as much of a punch. “Regardless of regardless of whether it’s a tropical storm or an extratropical program, the impacts are continue to heading to be the identical,” says Samantha Connolly, a meteorologist at the Countrywide Temperature Service’s business office in San Diego.
Even though people impacts include things like powerful winds, the largest threat will appear from torrential rains. The amount of money of rain could total three to six inches around a large space amongst Saturday and Monday, with some areas seeing as much as 10 inches. That a lot precipitation would pose a danger of flash floods any where but specifically in the dry soils of the desert. “It’s not heading to be absorbed extremely effectively,” Connolly suggests.
The possibility that torrents of h2o will operate down mountain slopes, engorge waterways, and flood streets and communities, implies residents ought to shell out awareness to their neighborhood temperature sources and alerts. And individuals need to steer clear of flood-vulnerable regions. “Rainfall flooding is responsible for most of the fatalities from tropical storms and hurricanes in the United States,” said NHC’s director Michael Brennan all through a dwell streamed briefing on Friday morning.
And due to the fact Hilary is a massive storm, those rains will start out slipping well ahead of its center tends to make landfall, Brennan stated.
Southern California and the broader Southwest are usually impacted by the remnants of tropical systems from the jap Pacific, Connolly claims. Just past calendar year the remnants of Hurricane Kay caused weighty rains, with ensuing flooding and mudflows, in California. But this will be a significantly potent event, Connolly adds.
California almost never sees immediate hits from tropical cyclones (the broad time period for tropical storms and hurricanes) mainly because prevailing atmospheric currents send out any storms that kind in the subtropics to the west and northwest. In the circumstance of the japanese Pacific Ocean, this atmospheric setup takes them absent from the continental U.S. The comparatively chilly waters off the West Coast also ordinarily result in any storms that do head towards land to weaken prior to they can make landfall. A hurricane struck San Diego, Calif., in Oct 1858, even so, and brought on significant harm.
In the scenario of Hilary, a robust location of superior pressure caught about the central portion of the U.S.—which will usher in a heat wave in all those areas—and a lower-strain place to the west of California are forcing Hilary a lot more northward, mentioned Daniel Swain, a local weather scientist at the College of California, Los Angeles, and the Nationwide Center for Atmospheric Investigate, throughout one of his regular “virtual local weather and climate office environment several hours,” hosted on YouTube. If you have a powerful storm relocating speedily together these types of a route, it might not drop aside as quickly as it normally would, placing up the uncommon probability of a tropical cyclone hitting the condition, he included.
When an El Niño is in location, as it is now, the local climate sample can ramp up hurricane activity in the japanese Pacific for the reason that it shifts atmospheric circulation designs in strategies that cut down the crosscutting winds that can hamper storm formation and strengthening around the area. (El Niño usually has the reverse impact in the Atlantic Ocean, where by it generally improves these winds, tamping down hurricane activity. But this yr exceptionally heat ocean waters are anticipated to override that impact, with NHC forecasting over-normal hurricane action there.)
Substantial investigate has concentrated on the opportunity effects of local weather alter on tropical cyclones. Broadly speaking, there is evidence that overall storm quantities could lower though storm depth may well improve, with a larger proportion of hurricanes in the much better categories. There is also proof that rainfall related with tropical cyclones will enhance with warming.
As to no matter if tropical programs could influence California much more routinely in a warmer long term, in his YouTube discuss, Swain mentioned that while this has not been formally researched to his awareness, such a circumstance is probable. “It’s been unusual historically, and it will most likely continue to be pretty unusual in the future but maybe rather a lot less so,” he stated. That is for the reason that of warming oceans. “There’s no way that southern California waters are going to heat high sufficient to support the progress of tropical cyclones, but the water off the coastline of Baja California will potentially heat sufficient to be less powerful at killing them off if they do variety and have this northward trajectory,” he additional. “So functions like this may develop into a little bit far more prevalent.”
[ad_2]
Source website link


