[ad_1]
Editor’s Note (8/21/23): This story is being republished since smoke from wildfires in western Canada is influencing air high quality throughout the Pacific Northwest.
The regular American could have now inhaled extra wildfire smoke in the to start with eight months of this year than for the duration of any the latest full year.
What is accountable for the history? Canada’s unparalleled blazes, which began in late April, have despatched plumes of smoke south to the U.S., impacting communities in the Midwest and along the East Coast that are unaccustomed to wildfires. This party is undermining a a long time-prolonged craze toward typically cleaner air in the U.S., driven by decades of minimized anthropogenic pollution. Now professionals hope the shock of 2023’s smoke will encourage collective and personal actions to minimize potential wildfire smoke exposure.
This 12 months “fire action has been around historic lows in most of the western U.S.,” says Marshall Burke, an economist at Stanford University. “Yet this will probably be the worst wildfire smoke calendar year on report in the U.S. and [is] solely due to Canadian fires. So that is actually new.”
Burke and his colleagues calculated that by early July, the ordinary American experienced been uncovered to practically 450 micrograms of smoke for each cubic meter (µg/m3). When they ran the exact same analysis again to 2006, they observed the largest publicity of those people decades arrived in 2021. More than the class of that 12 months, the normal American was exposed to just far more than 400 µg/m3, in section due to the fact of a specifically active fireplace period in the Rocky Mountains. The many years 2020 and 2022 also brought substantially previously mentioned-ordinary smoke publicity, which was pushed by fires in the western U.S. as effectively.
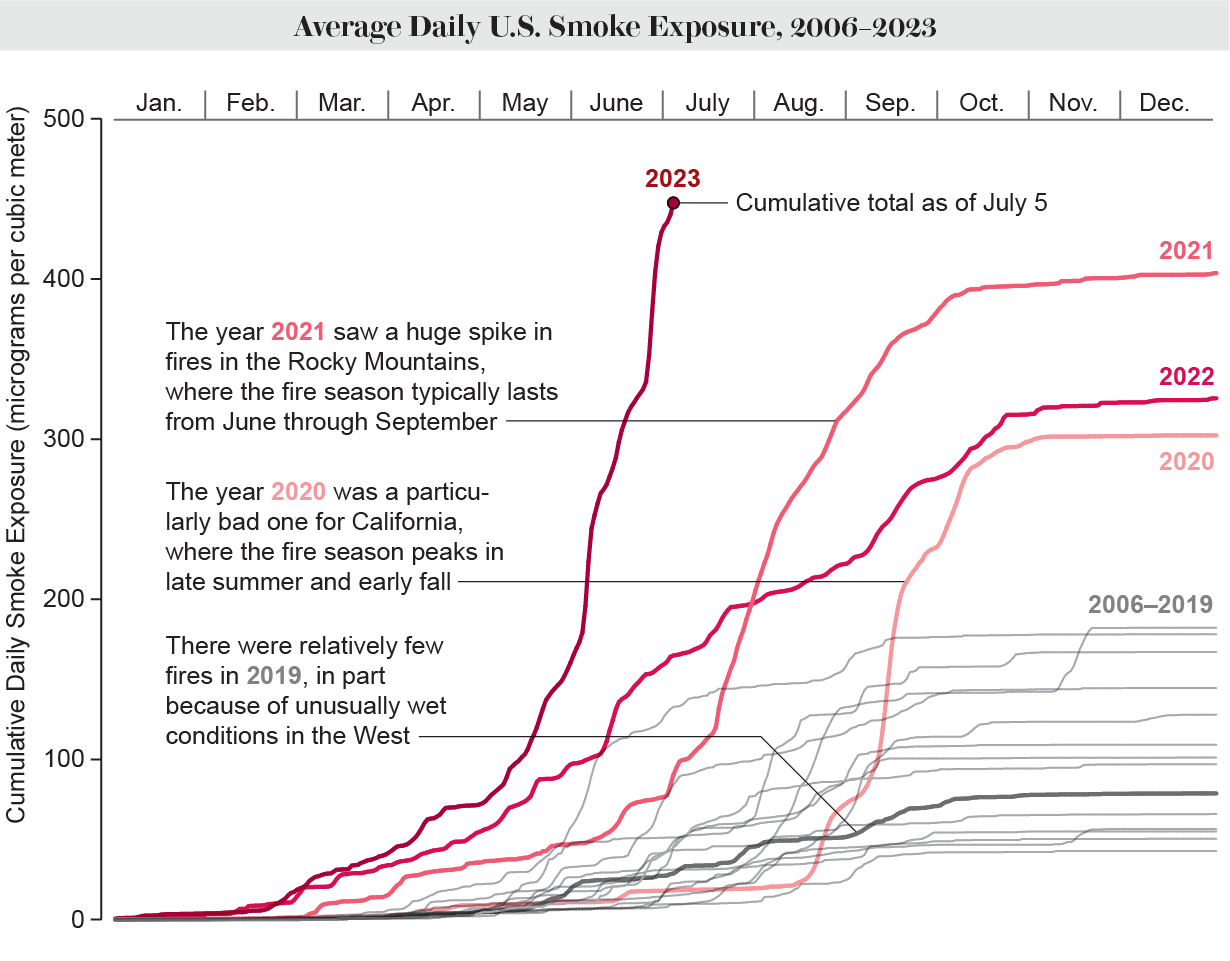


“That enhance in wildfire publicity is really reflective of not just extra fires but much more fires long lasting for for a longer time and impacting substantial populace areas—so just more men and women becoming uncovered to extra smoke for for a longer period intervals of time,” states Delphine Farmer, an atmospheric chemist at Colorado Point out University, who was not associated in the publicity assessment. “That development has been growing in excess of the past ten years, and I am unsurprised that we are hitting a optimum this yr.”
Burke and his colleagues relied on satellite data first gathered in 2006 to determine out wherever smoky skies predominated. By combining people data with common air air pollution measurements from sensors on the floor, they could determine how considerably of the smoke was lower in the ambiance, in which people today can breathe it in. Ultimately, the scientists included regional populace density to figure out about how a great deal smoke People in america were respiration.
The technique isn’t excellent, Burke and other folks note—surface sensors do not distinguish amongst wildfire smoke and other varieties of smaller particle pollution, these as that from neighborhood factories. And some gurus issue no matter if, for example, a median investigation that would be fewer affected by outliers would be a more meaningful approach than the national ordinary.
But the calculation is a single way to illustrate the remarkable character of this year’s fireplace season, Burke claims.
Usually U.S. wildfires—and the smoke they create—are contained in the West. But this yr a moist winter season has led to down below-normal fire activity in the West, while Canada has witnessed more than 5,000 fires melt away a lot more than 13 million hectares, according to Purely natural Resources Canada. Weather conditions designs have sporadically funneled smoke from fires in eastern Canada south around the densely populated Japanese Seaboard, quickly exposing large quantities of men and women to large amounts of smoke, albeit briefly.
“What’s troubling about this celebration is that so several, several folks have been impacted,” suggests Loretta Mickley, an atmospheric chemist at Harvard University, who wasn’t concerned in the publicity estimate.
With far more than 120 million individuals in the japanese and Midwestern U.S. exposed to that smoke, this year’s typical exposure soared, Burke states.
Wildfire smoke consists of very small particles that can travel deep into the overall body and wreak havoc, especially on the respiratory and cardiac techniques, says Carrie Redlich, a pulmonologist and occupational environmental drugs health practitioner at the Yale Faculty of Drugs, who was not concerned in the exposure analysis. There is even now a great deal that medical practitioners really do not know about the impacts of wildfire smoke, even so. A great deal of the study is based on normal air pollution, and it is challenging to tease apart the role smoke performed in any provided well being outcome, Redlich claims.
The impacts of quick bursts of high smoke publicity are even trickier to pinpoint. “For any presented individual, it’s not like their two times [of wildfire smoke are] likely to give them lung cancer compared to not,” Redlich states. “But when you multiply the risk in excess of thousands and thousands of men and women, which is what is happened, then there is the community overall health [concern].”
Christa Hasenkopf, an air top quality info skilled at the University of Chicago, who calculates the impression of air air pollution on lifestyle expectancy, claims that it takes about two months of superior air pollution to start out to see wellbeing impacts in these analyses. But she also emphasizes that some of the worst air high quality in the U.S. this summertime is a regular event in locations this sort of as Delhi. Globally, she claims, air air pollution lowered existence expectancy in 2020 by an common of about 2.2 many years. In the U.S. that number was 2.5 months, and the county with the worst air that year—Mariposa County, California—would working experience a 1.7-year lessen in daily life expectancy if people ailments turned the norm.
Authorities also underscore that even in the course of a remarkably undesirable yr for wildfire smoke, U.S. air is substantially cleaner than it has been. “Most of the steps would suggest that, on regular, the air is however a lot cleaner than it was even 15 many years ago or undoubtedly 30 yrs ago,” Burke suggests.
“The qualifications story listed here, which is seriously crucial, is the monumental accomplishment we have had in improving air top quality,” he states. But if smoke worsens, he warns, that all round photograph may possibly get started to change. “Wildfires are actually pushing back again on that quite difficult.”
Burke claims that the similar Clean up Air Act legislation that cleaned up ability generation and vehicles could be tailored to tackle wildfire smoke, which include by encouraging approved burns. These purposefully established and thoroughly monitored fires can minimize the odds of big, uncontrollable blazes by burning as a result of gas.
Farmer suggests she hopes this year’s high smoke exposure will stimulate just these types of routines. “We also have to have to know that we have the option to adjust and impression our wildfire smoke publicity, and we have tools that we can use,” Farmer states. Even people can just take motion to cut down their publicity by applying purifiers—even handmade kinds—to thoroughly clean indoor air.
“Could there be a dystopian foreseeable future? Well, indeed, there could,” Farmer claims. “But I assume we have to appear at it from the standpoint that we have resources we can implement to avoid that. I truly hope that this summer season is a wake-up connect with to policymakers and politicians and the public in standard to start thinking about these tools.”
[ad_2]
Supply website link


