[ad_1]
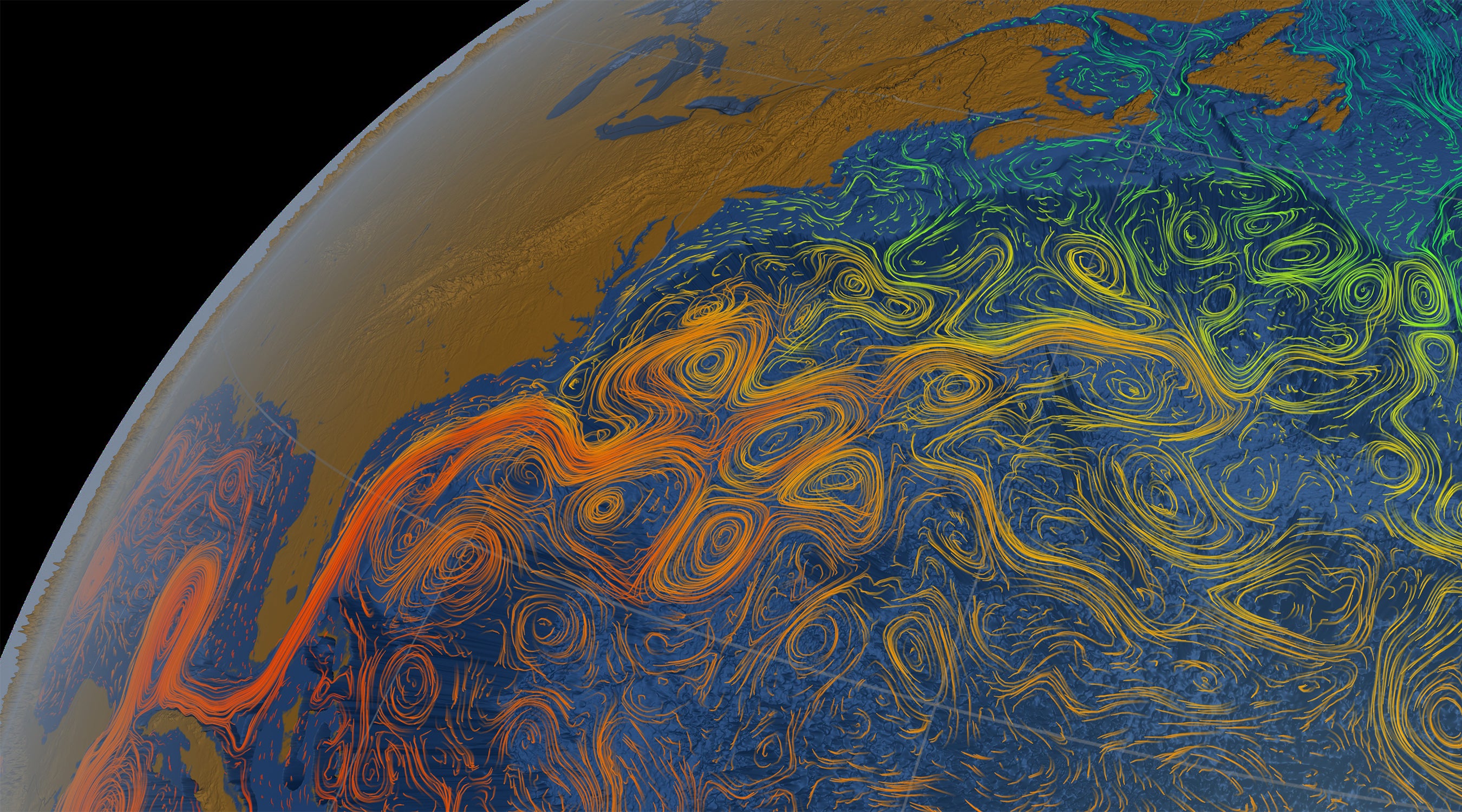
CLIMATEWIRE | An massive ocean current that warms some continents and cools some others as it snakes close to the environment could collapse a long time previously than experts predicted.
It would be a dire final result that disrupts temperature patterns in nearly each individual location on Earth. That will make the conclusions of a new research this 7 days alarming for the reason that of its timing. The present-day could shut down in as little as two several years — triggering chaotic climate improvements worldwide in authentic time.
But the locating is also controversial.
Preceding experiments have uncovered that the existing, recognized as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC, is weakening about time, but that it’s not likely to collapse ahead of the stop of the century. The new study marks the to start with time that researchers have attempted to pin down when the AMOC could halt doing the job — the authors stated it could be anytime among 2025 and 2095.
That raises new issues about the current’s vulnerability. But, to start with, let’s appear at the basics: What does the AMOC do, why is it significant in the context of local climate change, and what would happen if its circulation is interrupted?
What is the AMOC?
The AMOC (pronounced A-mock) is a gigantic ocean present-day procedure. It performs like an underwater conveyor belt that extends for thousands of miles to ferry warm surface area water from the equator towards the Arctic, where the drinking water cools and sinks to the base of the sea, in advance of flowing again in the opposite route and, at some point, welling up to the area yet again.
The rapid-flowing Gulf Stream, which surges past the U.S. East Coastline, is one particular portion of the technique. Additional branches of the AMOC extend into the Southern Hemisphere, where the identical overturning and upwelling course of action happens.
It’s a crucial component of the Earth’s local climate system. The AMOC helps distribute warmth all through the Atlantic Ocean basin, which in flip will help regulate local weather and climate patterns about the world. The heat water it carries via the North Atlantic, for occasion, is the purpose considerably of Europe is acknowledged for its delicate winters.
Why is it weakening?
Many studies have found that the AMOC is slowing down as time goes on. A single paper, published in 2021, estimated that the present-day is probable at its weakest stage in the previous 1,000 many years.
Some of the weakening may perhaps be pushed by purely natural versions in the Earth’s local weather technique — but human-caused climate transform is also to blame, scientists say. And climate styles, which simulate the Earth’s potential, recommend that continued warming could cause the program to get weaker.
Melting ice is a significant purpose. The large Greenland ice sheet, positioned in the middle of the North Atlantic, is pouring about 250 billion metric tons of ice into the ocean each and every yr on typical — and it truly is accelerating as the planet warms. This inflow of cold, contemporary drinking water into the sea can destabilize the AMOC’s flow over time.
If the current weakens adequate, it can finally cross a threshold of no return, resulting in the process to collapse. In fact, scientists feel it is occurred prior to. Research of the Earth’s historic weather suggest that the AMOC most likely shut down close to 13,000 several years in the past, all through a all-natural warming period when significant volumes of melting ice were being pouring into the ocean.
If it transpired in the past, it could come about yet again, industry experts alert. But the place the tipping issue is on the time scale and temperature arc is a big scientific discussion.
Weather designs have normally indicated that the AMOC will carry on to weaken in the coming many years but that it is really unlikely to thoroughly collapse in the subsequent 100 many years. The U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Local climate Change said in its most current assessment report that there was “medium confidence” the AMOC would not collapse in advance of the conclude of this century.
But some researchers say there is purpose to imagine conventional local weather models might be underestimating the AMOC’s weakening.
These authorities say the AMOC’s illustration in the versions is far too steady, explained David Thornalley, an ocean scientist and AMOC expert at University Faculty London. As a result, the styles could “underestimate the probability of an abrupt improve in AMOC,” he mentioned in an email to E&E News.
Stefan Rahmstorf, an ocean pro at the Potsdam Institute for Local climate Effects Exploration, mentioned local climate products also don’t sufficiently simulate the inflow of fresh new water from Greenland, a significant contribution to the slowing present-day.
That indicates the AMOC could weaken quicker than the types recommend.
What takes place if it collapses?
If the AMOC shuts down, it would have widespread worldwide consequences, researchers say.
Numerous scientific tests predict a significant cooling about parts of Europe, Thornalley explained — possibly by as significantly as 5 or 10 degrees Celsius. Tropical rain belts may well shift their positions, leading to some areas to practical experience far more droughts and many others to suffer far more floods.
Rahmstorf extra that the North Atlantic may well see a key raise in increasing seas. If the AMOC can not ferry big volumes of h2o all around the environment, the ocean may perhaps absorb fewer carbon dioxide from the environment. Areas of the deep ocean could receive significantly less oxygen. Marine ecosystems could modify in ways scientists are continue to seeking to have an understanding of.
In small, there could be extraordinary effects. But it is really nevertheless a issue of discussion whether or not those looming alterations could come about in just the next few decades.
Is the new study suitable?
The study posted this week indicates that the AMOC is probable to collapse inside of this century — and perhaps in just the up coming handful of years.
That getting conflicts with most previous research. As Rahmstorf and Thornalley pointed out, there is some evidence that the products may well be underestimating the AMOC’s weakening. But that does not suggest the new research overturns the narrative.
“No, I really don’t feel a single examine does overturn the IPCC evaluation, and we really should check out the results of this new study with some skepticism,” Thornalley said.
The research will take a various tactic from preceding modeling tries. It relies on observations of sea floor temperatures from just one area in the North Atlantic — then it employs a statistical method to extrapolate the upcoming of the full ocean program making use of these slender observations.
There are pros and cons to this tactic, professionals say.
The statistical process is audio, mentioned Levke Caesar, an AMOC professional at the College of Bremen in Germany, who commented on the new review for E&E News. But the research assumes that the whole AMOC can be adequately represented by employing observations from just a single region of the ocean.
In some strategies, it is challenging to get close to that issue. Researchers have only been checking the entire AMOC system with ocean sensors for a decade or so. Working with measurements from specific locations with extended facts sets is nonetheless important for these forms of reports.
But the assumption that these observations can represent the total process “needs to be further analyzed,” Caesar claimed.
There are other uncertainties about the information employed in the new examine, Thornalley additional. It relies on sea surface temperature measurements from 1 region in the subpolar North Atlantic and suggests that modifications in these temperatures are a type of “fingerprint,” or sign, of the shifting AMOC.
But Thornalley cautioned that the slowing AMOC could not be the only component that’s shifting this region of the ocean — and if which is the case, the study’s results may be considerably less robust.
On the other hand, Rahmstorf pointed out that the new research is not the only study to propose that the AMOC may well be weakening a lot quicker than researchers formerly envisioned.
A analyze published in 2021, and an additional just one released in 2022, also proposed that the AMOC might be approaching a tipping stage that could speed up its eventual collapse. These experiments didn’t go as much as to propose that a full collapse could be imminent within just a few several years — but they did show that the AMOC may perhaps be destabilizing speedier than anticipated.
“Individual experiments constantly have weaknesses and constraints, but when a number of studies with distinctive data and solutions stage to a tipping level that is already really close, I believe this possibility should really be taken very seriously,” Rahmstorf wrote in a current website article.
Caesar included that there are still questions about how the AMOC will behave as it weakens. It is attainable that the present could have several tipping details that lead to progressively weaker states but really don’t lead to the whole method to shut down.
“It could be that crossing the initially tipping issue does not lead to a total collapse of the AMOC, but that the system stabilizes at a weaker degree,” she mentioned.
On its very own, the hottest examine provides to a increasing physique of proof that the AMOC is in issues. But there are nevertheless a good deal of uncertainties about its actual findings, particularly the timeline it offers for collapse.
If all the inquiries and fears about the study’s solutions and assumptions could be addressed, “then this is a really concerning final result,” Thornalley stated.
But he added that “there are some actually major unknowns and assumptions that will need investigating ahead of we have self-confidence in this final result.”
Reprinted from E&E News with permission from POLITICO, LLC. Copyright 2023. E&E News delivers essential news for electricity and natural environment gurus.
[ad_2]
Source hyperlink

