[ad_1]
A meteorite that slammed into Mars in September 2021 has rewritten what researchers know about the planet’s interior.
By analysing the seismic vitality that vibrated as a result of the earth after the impression, scientists have found out a layer of molten rock that envelops Mars’s liquid-steel main. The getting, noted these days in two papers in Nature, signifies that the Martian core is lesser than previously imagined. It also resolves some lingering concerns about how the purple planet fashioned and developed above billions of several years.
The discovery will come from NASA’s Insight mission, which landed a craft with a seismometer on Mars’s area. Concerning 2018 and 2022, that instrument detected hundreds of ‘marsquakes’ shaking the world. Seismic waves made by quakes or impacts can gradual down or pace up dependent on what kinds of material they are travelling by way of, so seismologists can measure the waves’ passage to deduce what the inside of a earth seems like. On Earth, scientists have employed data from earthquakes to find the planet’s layers: a brittle outer crust, a typically solid mantle, a liquid outer core and a reliable internal core. Locating out regardless of whether other planets have related layers is important to knowing their geological historical past, including whether or not they had been at any time suitable for daily life.
InSight’s seismometer was the initially to detect marsquakes. In July 2021, on the foundation of the mission’s observations of 11 quakes, researchers noted that the liquid core of Mars appeared to have a radius of all-around 1,830 kilometres. That was greater than a lot of researchers had been anticipating. And it prompt that the main contained amazingly superior amounts of light-weight chemical factors, this kind of as sulfur, blended with iron.
But the September 2021 meteorite influence “unlocked every little thing,” says Henri Samuel, a geophysicist at the Institute of Earth Physics of Paris and guide creator of a single of today’s papers. The meteorite struck the planet on the aspect reverse to where by Perception was positioned. That’s a lot extra distant than the marsquakes that Perception had beforehand analyzed, and permitted the probe to detect seismic electricity travelling all the way by the Martian main. “We had been so thrilled,” states Jessica Irving, a seismologist at the College of Bristol, Uk, and a co-writer of Samuel’s paper.
Puzzle fixing
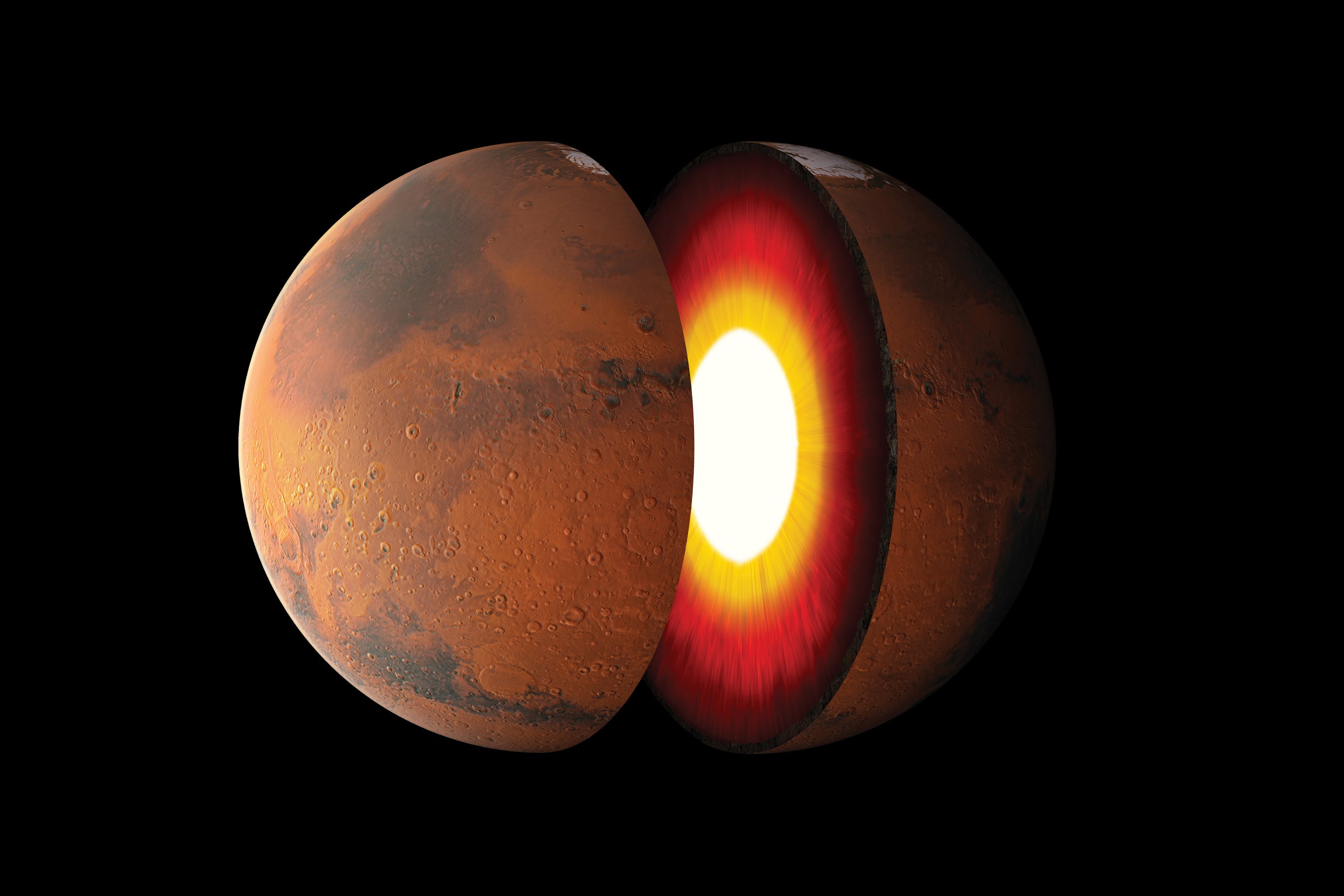
For Samuel, it was an chance to test his idea that a molten layer of rock surrounds Mars’s main. The way the seismic energy traversed the planet showed that what researchers experienced considered was the boundary among the liquid main and the reliable mantle, 1,830 kilometres from the planet’s centre, was essentially a different boundary among liquid and solid. It was the top of the newfound layer of molten rock meeting the mantle (see ‘Rethinking the Martian core’). The genuine core is buried beneath that molten-rock layer and has a radius of only 1,650 kilometres, Samuel claims.
The revised main measurement solves some puzzles. It signifies that the Martian core doesn’t have to incorporate high amounts of gentle components — a better match to laboratory and theoretical estimates. A 2nd liquid layer inside the earth also meshes better with other proof, this kind of as how Mars responds to currently being deformed by the gravitational tug of its moon Phobos.
“It’s an tasteful resolution,” says Simon Stähler, a seismologist at the Swiss Federal Institute of Engineering (ETH) Zurich who led the workforce that printed the 2021 paper. He stands by his team’s summary that it experienced noticed a deep boundary between liquid and sound it just turned out to be the leading of a molten-rock layer relatively than the prime of the liquid-metallic core.
Peculiar layering
The 2nd paper in Character today, from a staff impartial of Samuel’s, agrees that Mars’s core is enveloped by a layer of molten rock, but estimates that the core has a radius of 1,675 kilometres. The work analysed seismic waves from the exact same distant meteorite effect, as well as simulations of the attributes of mixtures of molten things this kind of as iron, nickel and sulfur at the superior pressures and temperatures in the Martian main. Possessing molten rock ideal up from molten iron “appears to be distinctive,” says lead writer Amir Khan, a geophysicist at ETH Zurich. “You have this peculiarity of liquid–liquid layering, which is anything that does not exist on the Earth.”
The molten-rock layer might be left over from a magma ocean that after lined Mars. As it cooled and solidified into rock, the magma would have left at the rear of a deep layer of radioactive things that still launch warmth and maintain rock molten at the foundation of the mantle, Samuel claims.
The Perception lander is now out of fee, its solar panels protected in dust, so it is unlikely that experts will get any evidence that could considerably revise Mars’s core dimension again any time soon. But evaluations of the mission’s previous observations may reveal some new specifics of what’s inside Mars.
This article is reproduced with permission and was very first released on October 25, 2023.
[ad_2]
Resource link


