[ad_1]
November 1, 2023
2 min study
From stray bullets to energy providers, people spark pretty much all of California’s wildfires

Flames eaten several properties as the Caldor Fireplace pushed into the Echo Summit region in California on August 30, 2021.
On a sweltering summer season day in 2021, fireplace abruptly swept by way of drought-dried underbrush and leaped throughout treetops in California’s Sierra Nevada. A neighborhood father and son, billed with setting up the 222,000-acre Caldor Hearth with their focus on-shooting products, are among the the countless numbers of people accused of igniting just about all the state’s forest fires because 2000. In addition to executives of utility businesses, whose faulty electrical devices has contributed to the state’s major and deadliest wildfires, the listing allegedly involves filth bikers who take away spark arresters and partners celebrating anniversaries with sky lanterns. “It’s human recklessness in 1 kind or another,” says Craig Thomas, founder of the nonprofit Fire Restoration Group.
California’s forests are progressively vulnerable to wildfires because of local climate change and poor forest administration. As for the actual ignitions, researchers have been documenting a gradual enhance in human involvement—but confronting the full extent of our accountability stays complicated. Statewide, 95 p.c of all wildfires are reportedly human-brought on. Thomas, along with Brent Skaggs, a retired U.S. Forest Support forest fire administration officer, made use of public Forest Company data to expose an astounding 19,543 wildfires attributed to human beings in between 2000 and 2022 on Forest Services land in California. It is not just campfires and cigarettes. Careless use of vans, chain saws or other products starts off virtually a quarter of the fires. Other people are induced by illegal fireworks, as effectively as electrical power generation, in accordance to company stats Thomas and Skaggs analyzed for Scientific American.
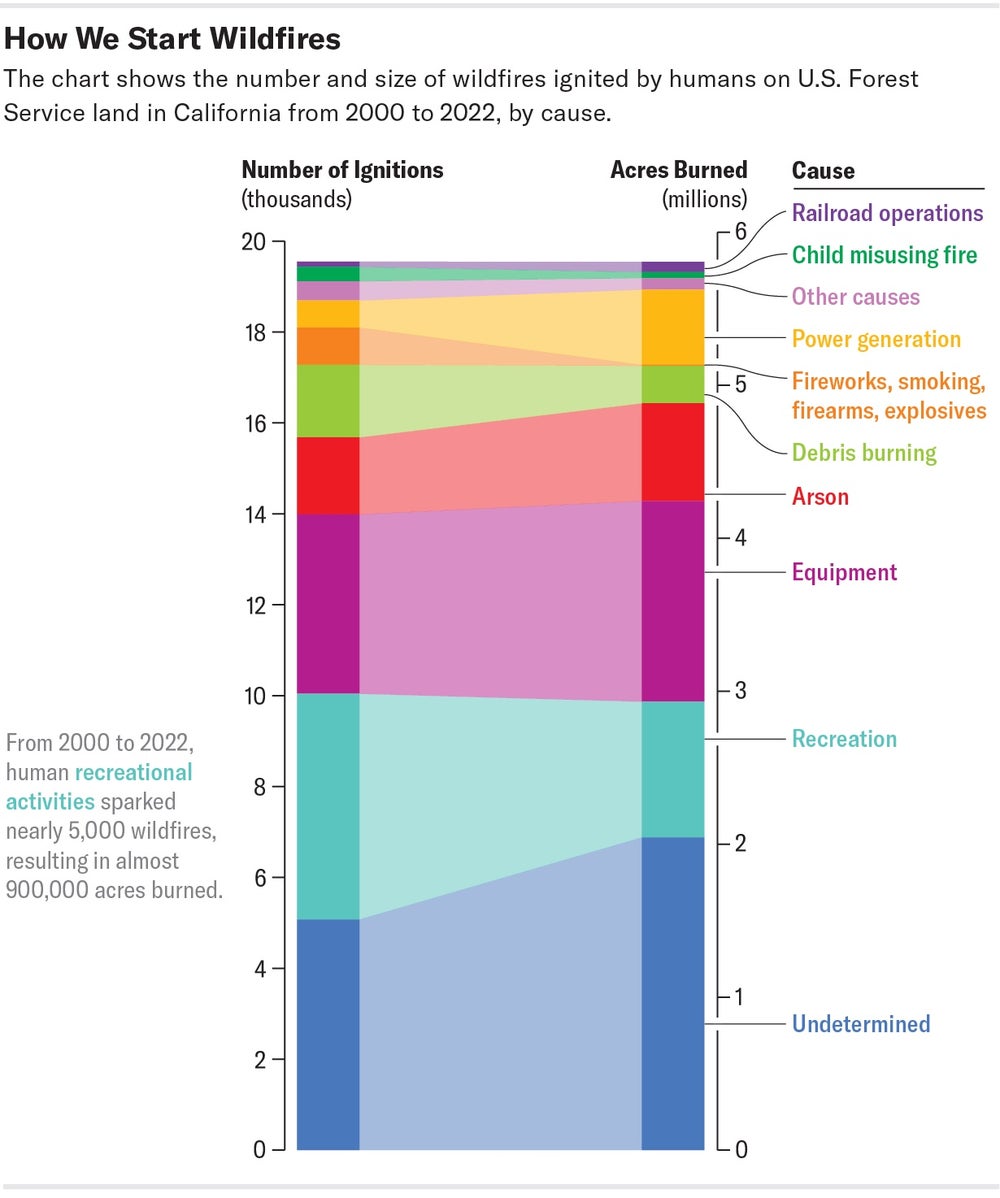
Hearth is a normal aspect of most forest ecosystems and has been all over significantly lengthier than human beings. For millennia, lightning sparked the large vast majority of wildfires—but currently it triggers just 5 p.c of California’s. And human-triggered blazes are likely to be additional destructive and fatal than people brought on by lightning they usually start out in close proximity to produced land with less trees and later on in the year when grasses are primarily combustible. California wildfires blamed on individuals involving 2012 and 2018 have been on regular 6.5 periods much larger than these caused by lightning strikes and killed three occasions as quite a few trees. They are also a lot more high-priced mainly because they tend to threaten houses—more than half of wildfire-combating fees arrive from defending residences.
Knowledge the sources of the sparks that get started the fires—not just the disorders that let them to spread—could support help you save life, properties and ecosystems, says Jennifer Balch, who studies fire ecology at College of Colorado Boulder. She emphasizes prevention in general public messaging and enforcement of guidelines built to decrease unlawful hearth commences. “We are the fireplace species,” Balch says. “We can do a great deal to adjust its study course on the landscape.”
With forests risky and climate significantly erratic, community accountability is critical. “Don’t be executing silly things in the woods,” Thomas states. “These forests can not tolerate human recklessness.”
[ad_2]
Supply url


