[ad_1]
Researchers have discovered no evidence that organic forces have contributed to our planet’s recent global warming challenge, but a center school student reading through a crisp new e-book from the nation’s prime science textbook publisher could possibly consider otherwise. “Due to the two human and normal actions,” the child would study, “the volume of carbon dioxide in the air has improved.”
That statement can be observed in McGraw Hill’s seventh-quality textbook Texas Science, a single of dozens of publications up for adoption in the state’s very first significant consideration of new science educational products since 2013. The Texas State Board of Education held its initial public listening to about the proposed resources on August 29 and is anticipated to make a ultimate choice about them after a second hearing in November. Textbooks that the board adopts will sit on classroom cabinets in Texas starting future tumble, and they are probably to impact textbooks throughout the state.
The books have already engendered controversy. Climate training advocates have requested the point out to adopt the new components due to the fact irrespective of their flaws, they involve considerable weather information that points out the science fundamental the local weather disaster the very last established of textbooks adopted by the point out a 10 years ago mainly did not. Yet some supporters of the fossil-gasoline marketplace, which include a congressional consultant, say the textbooks symbolize, in the words of that representative, an infiltration of “the radical climate lobby” into instruction, and have asked people today to force the point out to reject them.
The guides have been composed expressly to conform to Texas’s new science standards—expectations about what students study in each class and grade. When the Point out Board of Education up to date the standards in 2021, it selected to include things like information about the climate crisis in a essential class—middle university science—for the initial time in Texas historical past. As to start with described by Scientific American in 2022, nonetheless, the new local weather standards did not go as considerably as a lot of educators hoped. After a concerted campaign by the Texas Strength Council, an marketplace association that mainly represents oil and gas businesses, the board limited the breadth and depth of its new weather science specifications. This spring, as claimed by E&E News, the board took the added move of changing its textbook plan to explicitly favor books that emphasize fossil fuels’ “positive” features.
Due to the fact Texas is amid the premier textbook marketplaces in the U.S., the condition has experienced long-standing affect in excess of textbooks released nationwide. That signifies articles composed with Texan politics—and the state’s fossil-gasoline industry—in mind winds up in classrooms throughout the state. Textbooks usually have a extensive shelf lifestyle, so the permitted components will very likely be go through by small children into the 2030s.
The bulk of public remark at the hour-extensive community listening to on August 29 comprised testimony by local climate education advocates encouraging the board to approve the proposed publications as they are simply because for the most element, their material about the local weather disaster is exact and immediate. An 11th-quality college student who testified at the hearing, Marygrace Beinke, argued that it is essential that her fellow students—as properly as “our foreseeable future presidents, lecturers and scientists”—understand the danger the climate disaster poses. “Climate alter is not affected person or ineffable,” she mentioned. “It’s a straightforward lead to and impact, anything we can and have to prevent. Leaving these children blind to that—it’s not just inadequate sort but risky.”
Some users of the board appeared delicate to the effect that educating about weather transform would have on students’ perception of the oil and gas marketplace. Board member Will Hickman, who operates as an in-house legal professional for Shell Oil, questioned a testifier no matter whether instructional materials “should also consist of the benefits” of burning carbon. “We could flip the lights off and change off the air-conditioning in in this article. It’d be 110 levels, and we’d be sitting in the darkish,” he reported. “Is there a gain to turning the lights on, turning on the air-conditioning?” The testifier responded that Hickman had conflated the use of fossil fuels with the rewards of electricity, which can be produced with renewable resources.
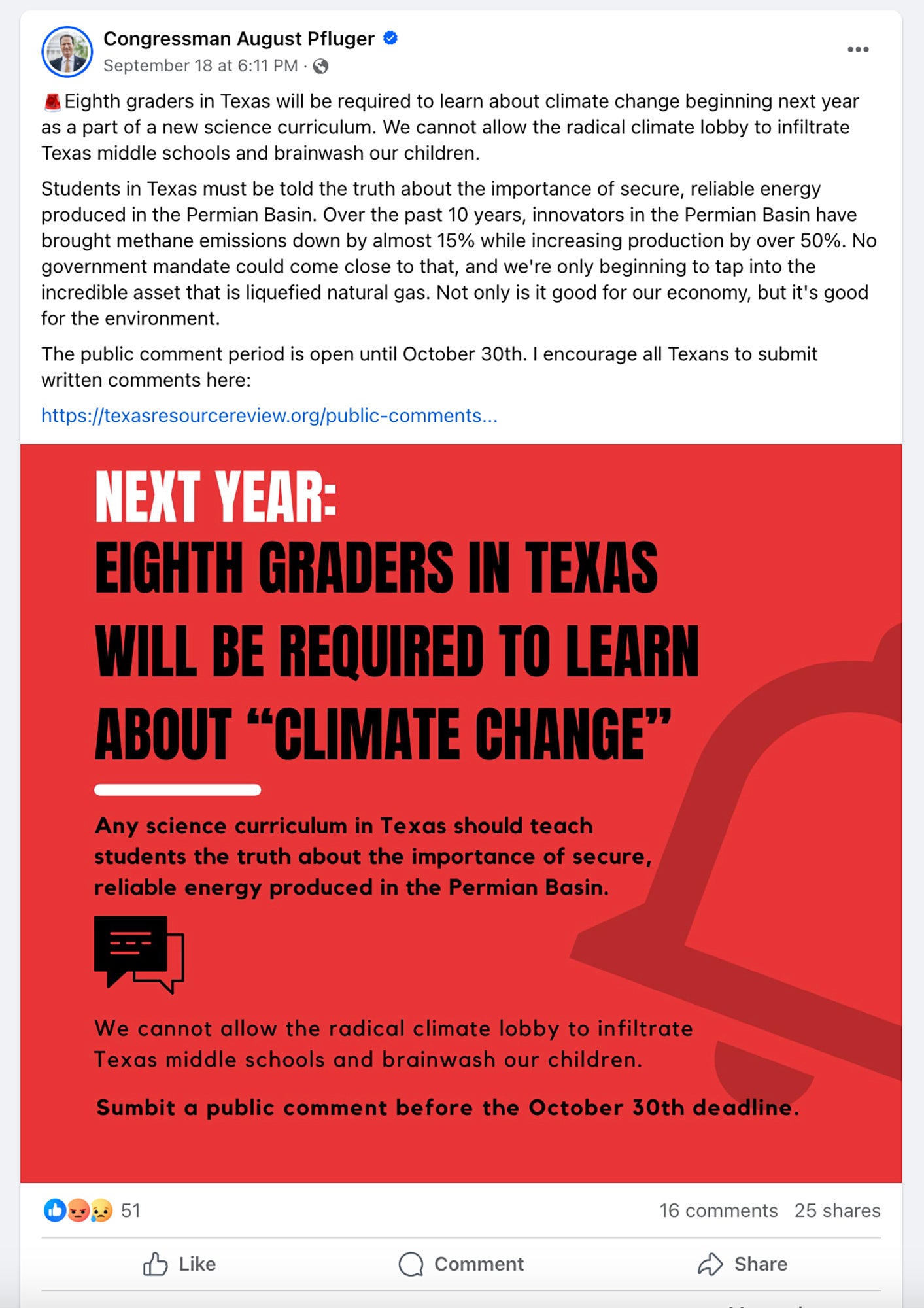
A couple of months following the assembly, the aforementioned congressperson, Representative August Pfluger of Texas, who represents a part of the state’s fossil-gasoline-loaded Permian Basin, wrote a submit on Facebook in which he asked for that his followers post a comment to the Condition Board of Education and learning inquiring for students to be taught “the truth of the matter about the value of protected, responsible strength generated in the Permian Basin.” He pointed out that the new science expectations need eighth graders to understand about climate adjust. “We can not enable the radical local weather foyer to infiltrate Texas middle educational facilities and brainwash our small children,” he wrote. Pfluger sits on the U.S. Dwelling Committee on Energy and Commerce. His office did not return a get in touch with for remark.

To study how political tensions have impacted the forthcoming textbooks, I reviewed the local weather material in the new center faculty science textbook sets set forth by the 3 premier K–12 publishers: McGraw Hill, Savvas Finding out Company (previously Pearson K12 Mastering) and Houghton Mifflin Harcourt (HMH), which with each other accounted for 4 of every five textbooks in U.S. general public center school science lecture rooms as of 2018. My evaluation located that the proposed new textbooks incorporate much a lot more sturdy facts about the climate disaster than their previously editions did. In some scenarios, even so, the textbooks appear to cloud the human brings about of the crisis.
Every of the 3 sets—McGraw Hill’s Texas Science, Savvas’s Texas Working experience Science and HMH’s Into Science Texas—place the bulk of their weather written content in a chapter of an eighth-grade science textbook. Overall, these respective chapters explain the latest local climate change’s system, effect and human origins without having equivocation. But in destinations, they appear to be to downplay the purpose of fossil fuels. Oil, gasoline and coal account for extra than 75 p.c of worldwide greenhouse fuel emissions, according to the United Nations, but the chapters every commit much more words on the contributions of deforestation, agriculture and urbanization than they do on fossil fuels. In locations, the guides lean on the phrase “releasing greenhouse gases” alternatively than “emitting greenhouse gases” or “burning fossil fuels.” The HMH e-book closes its chapter by highlighting the climate contributions of deforestation, urbanization and “carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases introduced by human routines.” Representatives from HMH did not answer to requests for remark about that language.
McGraw Hill’s eighth-grade local weather section starts with a scenario for college students to assess in which 4 good friends are speaking about modern climate change. A person suggests that though there is proof of people impacting the climate, it is “not viewed as scientific proof.” A second claims, “I think we now have proof that supports the idea that humans are influencing Earth’s climate.” A third implies that “we want more evidence,” though a fourth asserts that climate change “is a organic occasion. There is no evidence that human routines affect local climate.” The book instructs learners to evaluate which of the four figures they agree with.
Inquiring college students to debate the triggers of local climate change is not unusual: a lot more than fifty percent of science teachers across the U.S. say they teach the brings about of local climate alter as a discussion. Specialist local climate educators discourage this method, however, noting that it could leave pupils with the misunderstanding that the results in of the climate crisis are also debated by scientists, which they are not.
Outside the house of the eighth-grade chapters precise to latest climate transform, the topic appears in a smattering of other areas but not always robustly. In two spots, McGraw Hill’s seventh-grade reserve asserts that both of those human and purely natural actions have lately elevated carbon stages in the atmosphere. In a response to inquiries about Texas Science’s weather content material, a McGraw Hill representative reported that the business “is fully commited to developing accurate and productive academic components aligned to the requirements and curriculum demands of our shoppers. We extremely price the insight that our buyers and the public bring to conversations of our information throughout this adoption system, which is ongoing.”
A area in Savvas’s eighth-quality Texas Knowledge Science about how researchers find out about past climates by learning glaciers lists natural variables that have prompted the weather to change around the study course of time, which include “distance from the sun” and “ups and downs” in ocean temperature. “But these the natural way taking place activities do not solely reveal the Earth’s temperature changes in excess of the last number of centuries. Human pursuits are a different trigger,” the area states. “Greenhouse gases are actively playing a position in warming the world.”
In an e-mail to Scientific American, associates of Savvas defended this language, stating that it and other local weather content in the reserve are “fully aligned” with Texas’s new middle faculty science criteria and that Savvas is “committed to making sure our finding out answers give the instructors and pupils we serve with the most precise, relevant, actuality-based, and pedagogically audio content material.” Jesse Wilcox of the University of Northern Iowa, a co-writer of the textbook, wrote in an e-mail that “we identify people are triggering weather improve. We note in the curriculum that character, by alone, does not account for the local weather transform we are suffering from and that greenhouse gases are warming the earth. Whilst we want students to have an understanding of that our present-day local climate is a human-prompted problem, we also want learners to understand that natural variables (e.g., variations in radiation, orbital alterations, and volcanic eruptions) affect local weather. This is not a denial of human-prompted local weather change, but relatively, a more comprehensive comprehension of components that affect our local weather on Earth.”
The textbooks are nevertheless drafts and ended up initially submitted for public overview in April. As component of the adoption procedure, the Texas Education Agency organized two panels of reviewers to look at them. Neither established of panels asked for alterations to the local climate content of the three key textbook companies’ center college guides.
Nevertheless, when McGraw Hill presented the variations it planned to make to these drafts, it integrated tweaks to the eighth-grade local weather adjust material. In one situation, the authentic language reported:

“The principal way individuals have contributed to local weather transform is by burning fossil fuels to power vehicles and to produce electrical power. Burning the fuels releases carbon dioxide into the environment, which boosts the quantity of solar vitality that is trapped in the environment. Deforestation also increases carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to world-wide warming.”

In the edited version, this language was altered, and another reference to urbanization was additional:

“The primary way human beings have contributed to climate adjust is by burning fossil fuels to meet strength demand from customers. Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the ambiance. Deforestation and urbanization also boost carbon dioxide emissions, contributing to world wide warming.”

When requested about these and other proposed edits by Scientific American, a McGraw Hill representative mentioned adjustments had been manufactured for editorial good reasons, “such as clarity, length, regularity, and alignment to criteria.”
The preceding set of center university science textbooks McGraw Hill set up for adoption in Texas was termed iScience and posted in 2012. A guide in the established prompt that the cause of the local weather disaster was not totally understood: “Although a lot of researchers concur with” the U.N. Intergovernmental Panel on Weather Change’s summary that human industry has triggered the crisis, “some experts suggest that worldwide warming is because of to natural local climate cycles.” Editions of the textbook were being also offered in Alabama, Florida, Ga, Indiana, Massachusetts, Mississippi, New York, North Carolina, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia and Oklahoma. By 2018 versions of iScience sat on the cabinets of a quarter of American middle college science lecture rooms, all with that language intact. In 2021 when I requested why that and other inaccurate language about local climate alter experienced been prepared into their science textbooks, McGraw Hill reps responded that the articles had been published concerning 2007 and 2009, when, they said, the U.N. IPCC “was continue to in its infancy,” and the science for the human brings about of local weather alter wasn’t as settled as it is currently. Nevertheless the IPCC was fashioned in 1988 and issued its to start with warning about world-wide warming in 1990.
Two teams of local climate education and learning advocates, the Texas Liberty Network and the Nationwide Centre for Science Training (NCSE), performed their have joint evaluation of the proposed new textbooks’ weather content and located it general met the confined requirements of the new specifications. But in an interview, NCSE’s deputy director Glenn Department noted that “even the greatest of the textbooks have loads of room for advancement.”
Judy Dickey, a doctoral university student at Texas A&M’s Atmospheric Sciences method and previous high university trainer, was a single of the reviewers. She states the middle college textbooks left her with the perception that the publishers had watered down the contributions of fossil fuels to the crisis although overemphasizing the contributions of urbanization and deforestation.
“I do not know if this is intentional or not, but it felt like they ended up trying to change the blame to other international locations,” she states. “Deforestation and urbanization are not a North American problem, so it is like expressing that it is all these other evil nations around the world that are responsible for weather improve.”
The textbooks’ suggestions that nature is contributing to the disaster are “100 percent untrue,” Dickey claims, because although there are pure sources of greenhouse gases, the evidence implies the world would be in a cooling cycle if it ended up not for human emissions.
The Texas Point out Board of Schooling is envisioned to make its final decision about the textbooks at its upcoming meeting, which will just take place during the week of November 14. Texas citizens can submit composed opinions on the proposed textbooks until eventually Oct 30.
[ad_2]
Resource website link


